Overview of CPU Stress Testing
As technology progresses, the need for robust computing hardware becomes paramount. One way to ensure that a Central Processing Unit (CPU), the heart of any computer, is functioning at its best is through CPU stress testing. This method of evaluation pushes a CPU to its limits to assess its performance, stability, and thermal behavior under heavy loads.
The Purpose of CPU Stress Testing
CPU stress testing is crucial for a variety of reasons. Primarily, it plays a vital role in uncovering potential failures that could manifest under extreme conditions, helping users identify any weaknesses in their system that may not be immediately apparent. For overclockers, stress tests are particularly valuable as they can verify the stability of overclocked settings, ensuring that the system can handle the increased demands without compromising performance. Similarly, for manufacturers and system builders, these tests are essential to guarantee that the CPU can manage intense compute tasks over prolonged periods without overheating or crashing. This is crucial for both consumer satisfaction and product reliability. In essence, stress testing serves as a warranty that the CPU will perform as expected under the most demanding circumstances, providing users and manufacturers with confidence in the CPU’s capability to handle intensive workloads.
Factors to Consider When Conducting CPU Stress Tests
When performing CPU stress tests, various factors need to be taken into account to attain reliable and insightful results. Here are some critical considerations:
- Cooling System Efficacy: How well the cooling solution manages the thermal output during the test can significantly influence the CPU’s performance and life span.
- Duration of the Test: To effectively evaluate a CPU’s endurance, the stress test should be run for an adequate duration that could range from a few hours to an entire day.
- Type of Load: The stress test should simulate different types of workloads that the CPU might encounter in real-world usage scenarios, from gaming to rendering to scientific computations.
- Measurement Tools: Utilizing software to monitor temperatures, voltages, and clock speeds is necessary to gain insights into the CPU’s response under stress.
- Safety Measures: Ensuring safety protocols are in place is vital to prevent permanent damage to the CPU and other system components during the stress test.
Identifying the right tools and adhering to best practices during CPU stress testing will not only reveal a processor’s capabilities but also help in maintaining system health and longevity.
Top CPU Stress Test Tools of 2024
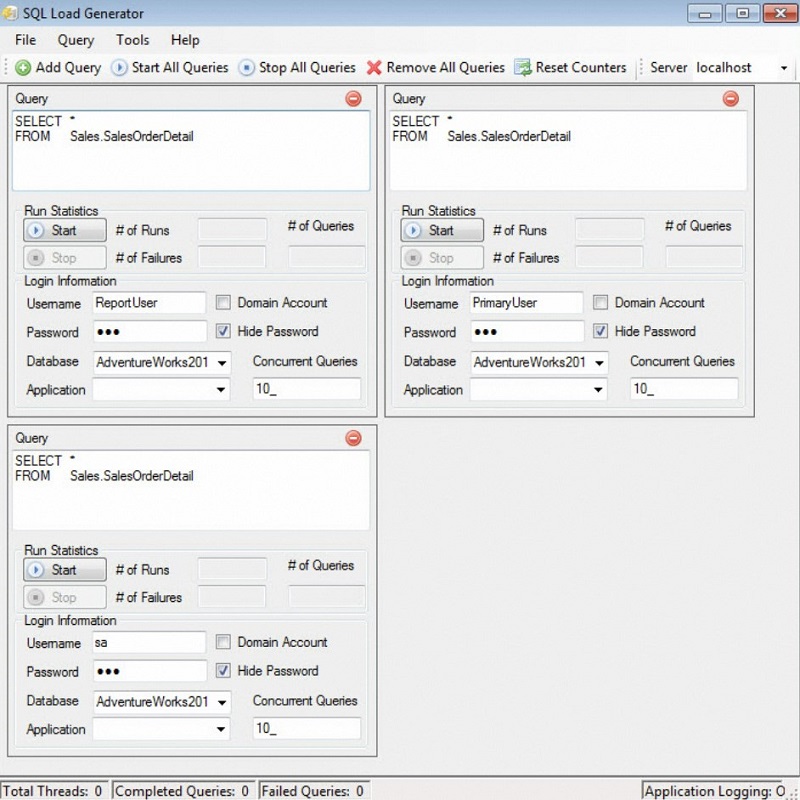
Selecting the right CPU stress test tool is crucial for effectively assessing the performance of a processor under extreme conditions. This year has brought us a range of tools, each with unique features, suited for different testing scenarios. Let’s explore some of the top CPU stress test tools of 2024 and what makes them stand out.
OCCT: Features and Limitations
OCCT stands out as a user-friendly and modern stress testing tool with a clean interface that provides real-time monitoring data on the CPU. Not only is it free for personal use, but it also offers detailed testing options that allow users to tweak testing parameters according to their needs. Despite its ease of use and comprehensive monitoring, OCCT has a limitation in its ability to run stress tests only up to an hour consecutively, nudging users toward its paid version for extended features.
Prime95: How It Works and Precautions
Prime95 is a classic in the CPU stress testing realm, well-known for its intense stress levels due to its method of searching for large prime numbers. While it offers various ‘torture tests’ that can highlight CPU and RAM stability, it is also infamous for putting extreme stress on CPUs, which could lead to higher-than-normal temperatures. Users must be cautious when using Prime95 and ensure their cooling systems are up to the task.
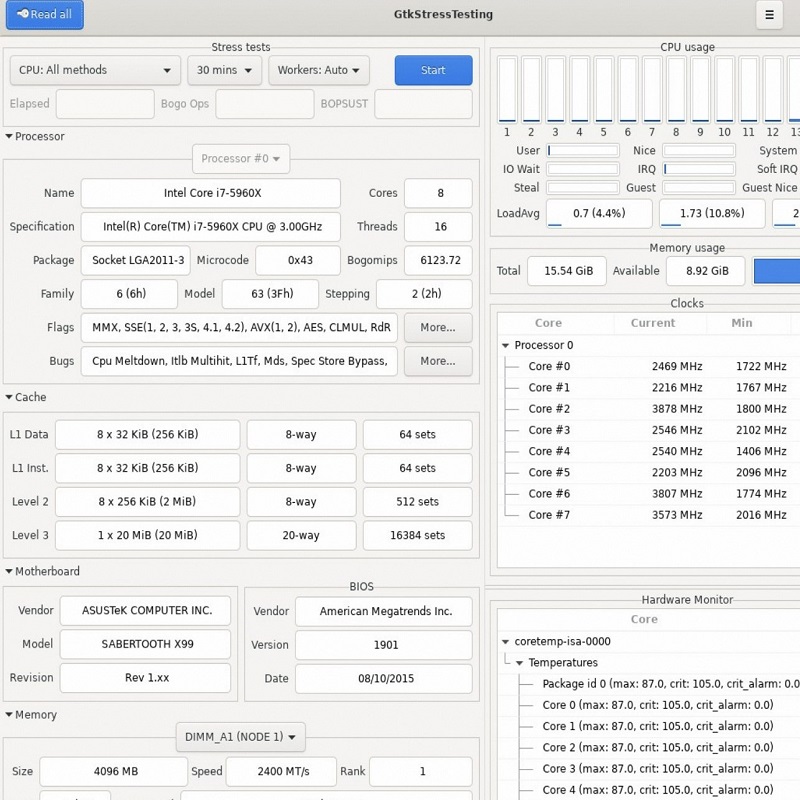
AIDA64: Premium Diagnostic Tool
For professionals who desire a comprehensive diagnostic and stress testing suite, AIDA64 offers a bevvy of features, albeit at a premium. Unlike other tools focused primarily on CPU load, AIDA64 provides a realistic workload simulation, including all system components. Although pricier, its ability to identify system bottlenecks and test component endurance makes it a valuable asset for enterprise testing scenarios.
Cinebench 2024: Realistic 3D Benchmarking
An industry favorite, Cinebench 2024, leverages the rendering of a complex 3D scene to provide a real-world benchmark for CPU performance. Its tests are designed to utilize all available CPU cores to their fullest, providing a measure of how a system will perform in processor-intensive tasks such as 3D rendering and content creation.
CPU-Z: Comprehensive System Information
While CPU-Z does emphasize CPU stress testing, its main feature is the detailed system information it provides. From processor name and manufacturing process to real-time core frequency readings, CPU-Z is a convenient tool for users who want to monitor their system’s specifications and performance during testing phases.
HeavyLoad: Versatility in Stress Testing
HeavyLoad offers a broad range of tests, making it a versatile tool for putting not just the CPU but also other components like GPU, RAM, and even storage under duress. Its graphical user interface (GUI) visualizes test processes, making it an attractive option for IT professionals who often need to validate multiple systems using a portable and accessible solution.
Choosing the right CPU stress test tool largely depends on the user’s needs, from basic stability checks to in-depth performance analysis. Each of these tools brings unique features to the table, catering to different segments of the tech world. By leveraging them effectively, one can gain valuable insights into the capabilities and limits of their CPU.
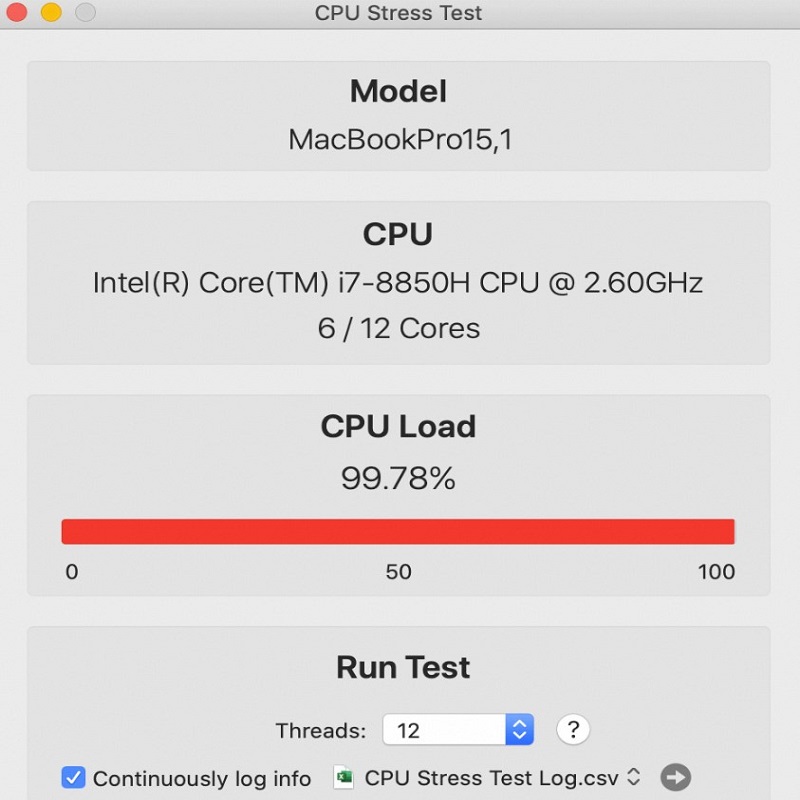
Monitoring and Safety During Stress Tests
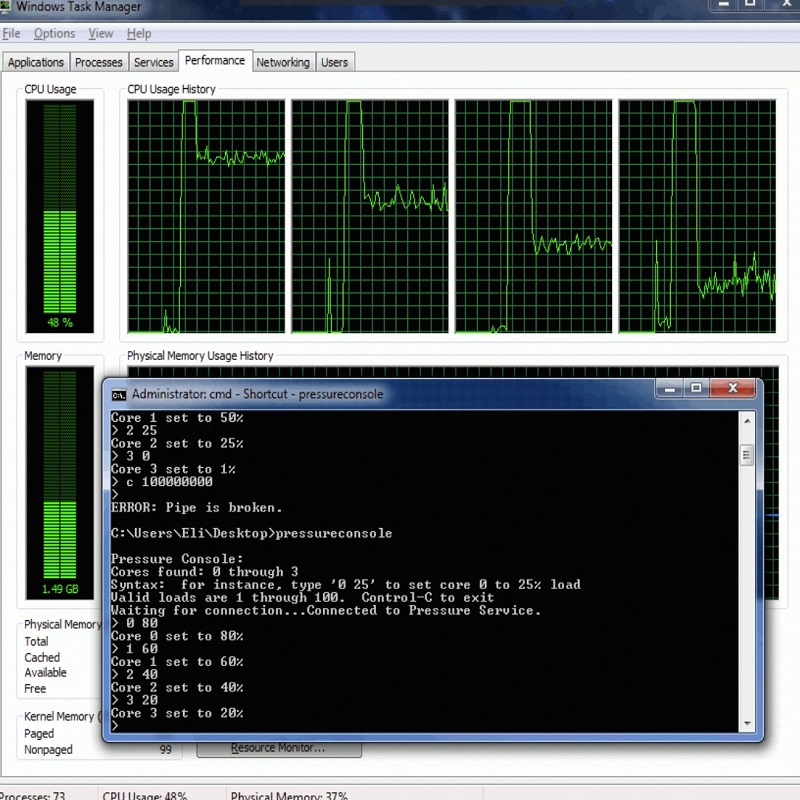
Conducting CPU stress tests is not just about pushing a processor to its limits; it’s also about doing so responsibly. This requires careful monitoring of the CPU’s temperature and power draw, both to ensure the CPU is performing within safe operational parameters and to prevent damage to the hardware. Let’s delve into the importance of these aspects and consider the tools and best practices that surround safe CPU stress testing.
Importance of Monitoring Temps and Power Draw
During a stress test, a CPU is subjected to intense workloads that can significantly increase its temperature and power consumption. If these parameters exceed certain thresholds, it can lead to thermal throttling, where the CPU automatically lowers its frequency to reduce heat, or in extreme cases, permanent damage to the processor.
Continuous monitoring allows you to observe how the CPU handles stress and if the cooling system is adequately dissipating heat. Power draw monitoring is equally crucial because it can provide insights into the efficiency of your power supply and the stress on your system’s electrical components. Recognizing the signs of power or thermal issues during a test can help you take timely action to mitigate risks.
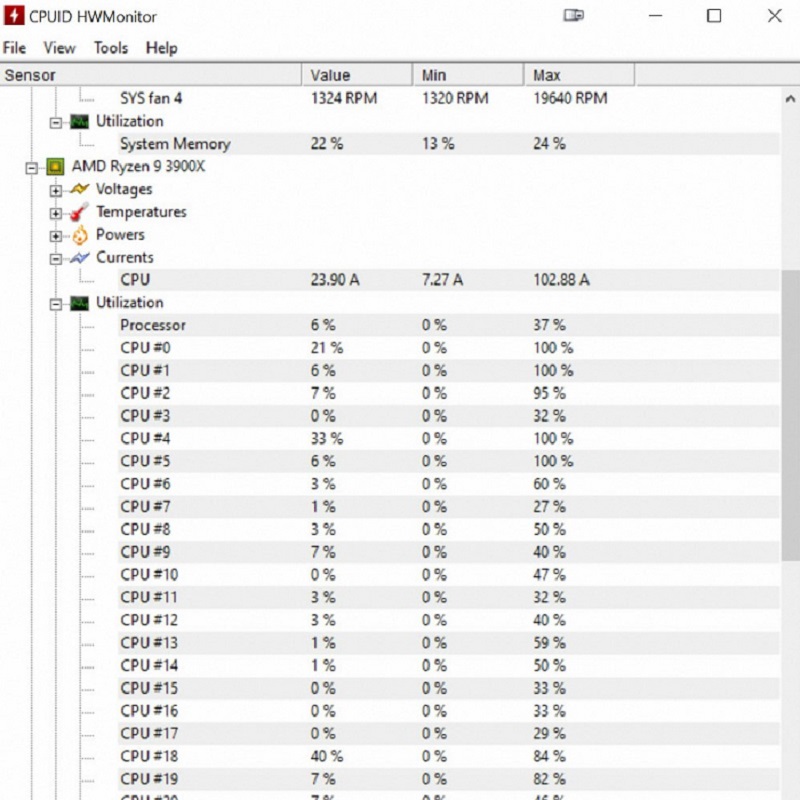
Recommended Monitoring Tools
When stress testing, it is recommended to use supplementary monitoring tools that can track a wide range of data points. Some highly regarded options include HWMonitor, HWiNFO64, and Core Temp. These tools often provide real-time updates on key metrics like temperatures across CPU cores, fan speeds, voltage, and clock speeds.
Using such software allows you to:
- Check if all cores are being evenly stressed.
- Verify that temperatures remain within safe limits throughout the testing process.
- Ensure that your cooling system is effective.
- Observe any fluctuations in clock speeds that could indicate instability or throttling.
Pairing these monitoring tools with your stress test software can give you a complete picture of your CPU’s performance under pressure and is essential for conducting thorough and safe evaluations.
Precautions and Safe Stress Testing Practices
To safely conduct a CPU stress test, one must follow certain precautions:
- Start with a Clean System: Ensure that the CPU and its cooling system are dust-free and that thermal paste is properly applied.
- Optimal Ventilation: Make sure that the PC case has good airflow, with no obstruction to intake or outtake fans.
- Monitor Progress: Keep a close eye on the monitoring tools and stop the test if temperatures get dangerously high or if you detect power supply issues.
- Gradual Overclocking: If testing an overclock, increase the frequency and voltage in small increments to prevent sudden overloads.
- Emergency Plan: Have a plan to immediately shut down the system if something goes wrong.
Embracing these practices will not only ensure that you collect valuable data about your CPU’s performance but also safeguard the hardware from the potential perils of extreme stress testing. For seasoned professionals and novices alike, responsible monitoring is the cornerstone of any serious stress testing regimen.